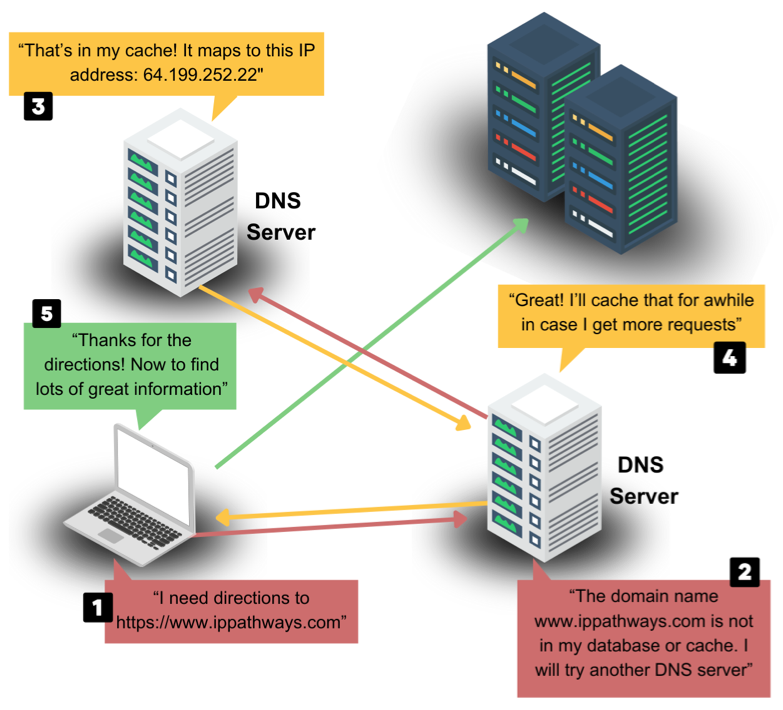
DNS stands for Domain Name System. It is a system that translates domain names into IP addresses, which computers use to identify each other on the internet. When you enter a URL in your web browser, your computer requests a DNS server to look up the IP address associated with that domain name. The DNS server then sends the IP address back to your computer, allowing it to connect to the website. DNS works through a hierarchy of servers, with the top-level servers containing information about the root domain names (like .com, .org, etc.) and the lower-level servers containing information about specific domain names. This allows for efficient and accurate translation of domain names into IP addresses, which is essential for the functioning of the internet. Without DNS, the internet as we know it would be impossible.
Why is DNS Security Important?
The DNS system is vulnerable to numerous cyber threats due to its design limitations and lack of security measures. Such hazards include spoofing, amplification, DoS, and the interception of private information. Moreover, DNS attacks are often used as a distraction tactic with other cyberattacks, making it harder for a security team to focus on a potentially more significant threat. With these vulnerabilities, it is essential to have strong DNS security to prevent DNS attacks and protect business continuity.
DNS Security Threats
Denial of Service (DoS)
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks are a common type of cyber-attack that can be used to disrupt the normal functioning of a domain name system (DNS). In a DoS attack, a threat actor floods a DNS server with a large traffic volume, causing it to become overwhelmed and stop responding to legitimate DNS requests.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
One common DoS attack type is known as a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack. In a DDoS attack, multiple systems are used to flood a DNS server with traffic, making it much more difficult to mitigate the attack. Whereas a DoS attack is an attack from one spot, not multiple. DDoS attacks can be particularly challenging to defend against, as they can involve many compromised systems and come from many different sources.
A DoS and DDoS attack can have negative consequences, including website downtime, lost revenue, and reputational damage.
DNS Spoofing (DNS Cache Poisoning)
In this type of DNS attack, hackers redirect internet traffic from legitimate websites to fraudulent ones, which can result in data theft, financial fraud, and other malicious activities. DNS spoofing works by altering the DNS cache of a user’s computer or the DNS server, replacing the IP address of a legitimate website with that of a fraudulent website. As a result, when users try to access a legitimate website, they are directed instead to a fraudulent one, where their sensitive information may be stolen, or malware can be distributed.
DNS Tunneling
DNS tunneling is a technique hackers use to bypass security measures and steal data. It involves encoding data into DNS queries and responses to create a covert communication channel through a DNS server. This technique allows hackers to bypass firewalls and other security measures that may block other types of communication channels. While DNS tunneling can also be used for legitimate purposes, when used maliciously, it poses a significant threat to data security.
DNS Amplification
DNS Amplification is a type of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack that is used by cybercriminals to overwhelm a website’s servers with traffic. This attack is carried out by exploiting the way the Domain Name System (DNS) works.
In a DNS Amplification attack, the attacker spoofs the victim’s IP address and sends a query to a DNS server with a spoofed IP address, requesting a significant DNS response. The server then returns a large DNS response to the victim’s IP address, much larger than the original query packet. This amplification of the DNS response causes the victim’s network to be flooded with traffic, ultimately leading to a Denial of Service (DoS) attack.
DNS Hijacking
DNS hijacking is a technique used by cybercriminals to redirect users to a malicious website instead of the intended site. In this attack, the attacker gains access to the DNS server, which is responsible for translating domain names into IP addresses. The attacker then changes the DNS records of the targeted domain to point to a different IP address, which is under the attacker’s control.
Because of this attack, users are redirected to the attacker’s website when they try to access it instead. This can be a severe security issue as the attacker can steal sensitive information, inject malware, or perform other malicious activities.
DNS hijacking differs from DNS spoofing in that hijacking involves changing the DNS settings, and DNS spoofing involves modifying DNS records.
How to Mitigate DNS Security Threats
A working DNS allows people to access their apps and services for personal and professional use, whether hosted locally or in the cloud. If DNS is compromised, users cannot perform their day-to-day tasks, and therefore, no business can be done. DNS security is a first-line defense to prevent any of the common DNS attacks listed above from becoming a more significant cybersecurity problem.
1. DNSSEC
DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC) is a set of protocols that adds an extra layer of security to DNS. DNSSEC uses digital signatures and encryption to ensure the authenticity and integrity of DNS data. With it, users can verify that the DNS data they receive is legitimate and has not been tampered with. DNSSEC can prevent DNS spoofing and other attacks that rely on falsifying DNS data.
2. DNS Filtering
DNS filtering is another effective DNS security method that blocks access to malicious websites and other online resources. This method uses a blocklist of known malicious domains and IP addresses. When a user tries to access a website on the blocklist, the DNS resolver blocks the connection, preventing the user from accessing the site.
3. DNS Firewall
A DNS firewall is designed to protect DNS traffic. DNS firewalls work by blocking connections to known malicious domains and IP addresses. A DNS firewall can also block contacts from specific countries or regions known for hosting malicious content. DNS firewalls can be deployed as standalone appliances or as software on DNS servers.
4. DNS Audits/ Anomaly Detection
Regular audits of DNS settings and records can confirm they have not been altered. They can help identify vulnerabilities and outdated records that can be cleaned up for a more efficient system.
An anomaly detection system can help identify unusual patterns or behavior in your network traffic. This can alert the security team for timely mitigation of the potential threat, or an automated solution can respond on its own in real time.
Other DNS Security Best Practices:
- Using a VPN
- Implementing MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication)
- Employ firewalls and antivirus software
- Conduct risk assessments
- Employee cybersecurity training sessions
- Strengthen passwords
DNS security is critical for protecting networks and users from cyber threats. DNSSEC, DNS filtering, DNS firewalls, DNS audits, and anomaly detection are some of the most effective DNS security methods that can help you protect your network from attacks. By implementing these measures, you can ensure the authenticity, integrity, and availability of DNS services and protect your network from cybercriminals.
At IP Pathways, we understand the security risks of a cyber-attack. In partnership with Tenax Solutions, an IP Pathways Company, we are happy to offer security and compliance services to uniquely support you and your team. Our experienced engineers will work with you to understand your goals and provide custom solutions that cater to your needs. We offer various security services, including risk management and assessment, penetration testing, offensive security, and remediation services. IP Pathways can also implement backup as a service, managed Cisco Duo, and firewall as a service to develop a holistic security solution. Check out our complete list of services here and contact us today!
IP Pathways
Cloud Services | Managed Services | IT Solutions | IT Consulting
At IP Pathways, we understand how difficult it is to scale on your own. But what if you could move past the issues currently holding you back? Good news–you can! We identify opportunities in your organization to leverage technology to spark greater growth starting now. Our tailored solutions turn IT into a strategic investment rather than a cost center. With the right tech, you can move faster, innovate, and gain a competitive edge.
Our engineers have deep technical expertise and experience. They architect, implement, monitor, support, and manage custom technology solutions for organizations using only the highest-quality and best-in-class systems. As a result, projects are completed on time and within budget, ready to deliver the results you need to fuel your organization forward. Contact Us